Agents and Tools
Workflow steps can call agents to leverage LLM reasoning or call tools for type-safe logic. You can either invoke them from within a step's execute function or compose them directly as steps using createStep().
Using agents in workflowsDirect link to Using agents in workflows
Use agents in workflow steps when you need reasoning, language generation, or other LLM-based tasks. Call from a step's execute function for more control over the agent call (e.g., track conversation history or return structured output). Compose agents as steps when you don't need to modify how the agent is invoked.
Calling agentsDirect link to Calling agents
Call agents inside a step's execute function using .generate() or .stream(). This lets you modify the agent call and handle the response before passing it to the next step.
const step1 = createStep({
// ...
execute: async ({ inputData, mastra }) => {
const { message } = inputData;
const testAgent = mastra.getAgent("testAgent");
const response = await testAgent.generate(
`Convert this message into bullet points: ${message}`,
{
memory: {
thread: "user-123",
resource: "test-123",
},
},
);
return {
list: response.text,
};
},
});
Agents as stepsDirect link to Agents as steps
Compose an agent as a step using createStep() when you don't need to modify the agent call. Use .map() to transform the previous step's output into a prompt the agent can use.
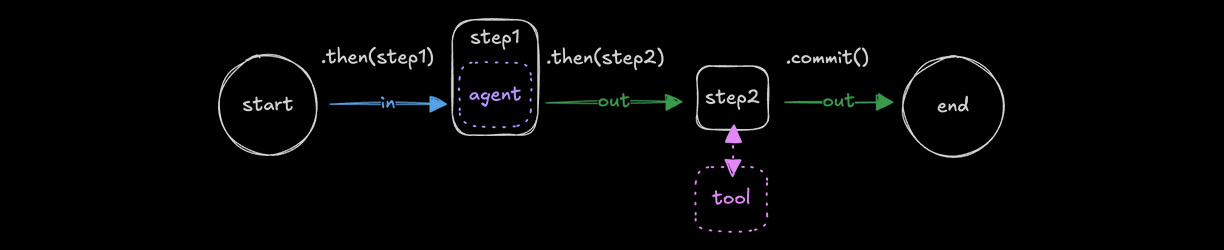
import { testAgent } from "../agents/test-agent";
const step1 = createStep(testAgent);
export const testWorkflow = createWorkflow({
// ...
})
.map(async ({ inputData }) => {
const { message } = inputData;
return {
prompt: `Convert this message into bullet points: ${message}`,
};
})
.then(step1)
.then(step2)
.commit();
See .map() for more information.
Mastra agents use a default schema that expects a prompt string as input and returns a text string as output:
{
inputSchema: {
prompt: string
},
outputSchema: {
text: string
}
}
Using tools in workflowsDirect link to Using tools in workflows
Use tools in workflow steps to leverage existing tool logic. Call from a step's execute function when you need to prepare context or process responses. Compose tools as steps when you don't need to modify how the tool is used.
Calling toolsDirect link to Calling tools
Call tools inside a step's execute function using .execute(). This gives you more control over the tool's input context, or process its response before passing it to the next step.
import { testTool } from "../tools/test-tool";
const step2 = createStep({
// ...
execute: async ({ inputData, runtimeContext }) => {
const { formatted } = inputData;
const response = await testTool.execute({
context: {
text: formatted,
},
runtimeContext,
});
return {
emphasized: response.emphasized,
};
},
});
Tools as stepsDirect link to Tools as steps
Compose a tool as a step using createStep() when the previous step's output matches the tool's input context. You can use .map() to transform the previous step's output if they don't.
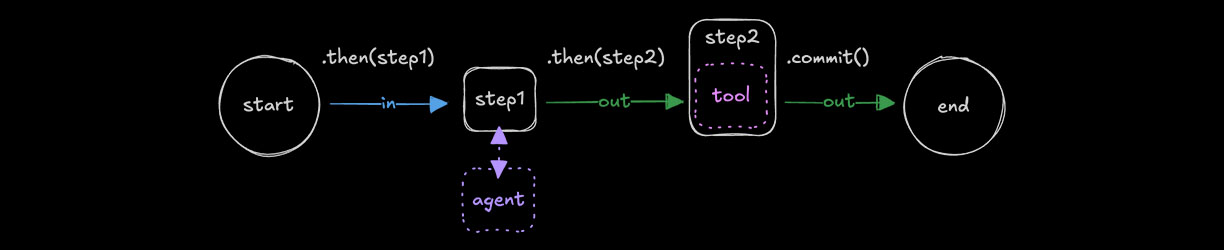
import { testTool } from "../tools/test-tool";
const step2 = createStep(testTool);
export const testWorkflow = createWorkflow({
// ...
})
.then(step1)
.map(async ({ inputData }) => {
const { formatted } = inputData;
return {
text: formatted,
};
})
.then(step2)
.commit();
See .map() for more information.