Workflows overview
Workflows let you define complex sequences of tasks using clear, structured steps rather than relying on the reasoning of a single agent. They give you full control over how tasks are broken down, how data moves between them, and what gets executed when. Workflows run using the built-in execution engine by default, or can be deployed to workflow runners like Inngest for managed infrastructure.
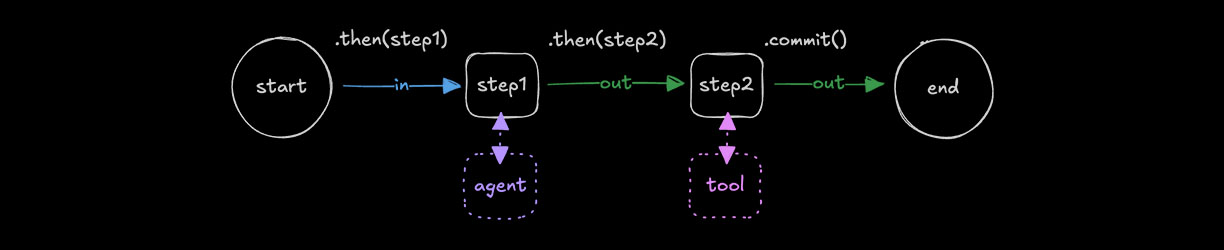
When to use workflowsDirect link to When to use workflows
Use workflows for tasks that are clearly defined upfront and involve multiple steps with a specific execution order. They give you fine-grained control over how data flows and transforms between steps, and which primitives are called at each stage.
An introduction to workflows, and how they compare to agents YouTube (7 minutes)
Core principlesDirect link to Core principles
Mastra workflows operate using these principles:
- Defining steps with
createStep, specifying input/output schemas and business logic. - Composing steps with
createWorkflowto define the execution flow. - Running workflows to execute the entire sequence, with built-in support for suspension, resumption, and streaming results.
Creating a workflow stepDirect link to Creating a workflow step
Steps are the building blocks of workflows. Create a step using createStep() with inputSchema and outputSchema to define the data it accepts and returns.
The execute function defines what the step does. Use it to call functions in your codebase, external APIs, agents, or tools.
import { createStep } from '@mastra/core/workflows'
const step1 = createStep({
id: 'step-1',
inputSchema: z.object({
message: z.string(),
}),
outputSchema: z.object({
formatted: z.string(),
}),
execute: async ({ inputData }) => {
const { message } = inputData
return {
formatted: message.toUpperCase(),
}
},
})
Visit Step Class for a full list of configuration options.
Using agents and toolsDirect link to Using agents and tools
Workflow steps can also call registered agents or import and execute tools directly, visit the Using Tools page for more information.
Creating a workflowDirect link to Creating a workflow
Create a workflow using createWorkflow() with inputSchema and outputSchema to define the data it accepts and returns. Add steps using .then() and complete the workflow with .commit().
import { createWorkflow, createStep } from "@mastra/core/workflows";
import { z } from "zod";
const step1 = createStep({...});
export const testWorkflow = createWorkflow({
id: "test-workflow",
inputSchema: z.object({
message: z.string()
}),
outputSchema: z.object({
output: z.string()
})
})
.then(step1)
.commit();
Visit Workflow Class for a full list of configuration options.
Understanding control flowDirect link to Understanding control flow
Workflows can be composed using a number of different methods. The method you choose determines how each step's schema should be structured. Visit the Control Flow page for more information.
Workflow stateDirect link to Workflow state
Workflow state lets you share values across steps without passing them through every step's inputSchema and outputSchema. Use state for tracking progress, accumulating results, or sharing configuration across the entire workflow.
const step1 = createStep({
id: 'step-1',
inputSchema: z.object({ message: z.string() }),
outputSchema: z.object({ formatted: z.string() }),
stateSchema: z.object({ counter: z.number() }),
execute: async ({ inputData, state, setState }) => {
// Read from state
console.log(state.counter)
// Update state for subsequent steps
setState({ ...state, counter: state.counter + 1 })
return { formatted: inputData.message.toUpperCase() }
},
})
Visit Workflow State for complete documentation on state schemas, initial state, persistence across suspend/resume, and nested workflows.
Workflows as stepsDirect link to Workflows as steps
Use a workflow as a step to reuse its logic within a larger composition. Input and output follow the same schema rules described in Core principles.
const step1 = createStep({...});
const step2 = createStep({...});
const childWorkflow = createWorkflow({
id: "child-workflow",
inputSchema: z.object({
message: z.string()
}),
outputSchema: z.object({
emphasized: z.string()
})
})
.then(step1)
.then(step2)
.commit();
export const testWorkflow = createWorkflow({
id: "test-workflow",
inputSchema: z.object({
message: z.string()
}),
outputSchema: z.object({
emphasized: z.string()
})
})
.then(childWorkflow)
.commit();
Cloning a workflowDirect link to Cloning a workflow
Clone a workflow using cloneWorkflow() when you want to reuse its logic but track it separately under a new ID. Each clone runs independently and appears as a distinct workflow in logs and observability tools.
import { cloneWorkflow } from "@mastra/core/workflows";
const step1 = createStep({...});
const parentWorkflow = createWorkflow({...})
const clonedWorkflow = cloneWorkflow(parentWorkflow, { id: "cloned-workflow" });
export const testWorkflow = createWorkflow({...})
.then(step1)
.then(clonedWorkflow)
.commit();
Registering a workflowDirect link to Registering a workflow
Register your workflow in the Mastra instance to make it available throughout your application. Once registered, it can be called from agents or tools and has access to shared resources such as logging and observability features:
import { Mastra } from '@mastra/core/mastra'
import { testWorkflow } from './workflows/test-workflow'
export const mastra = new Mastra({
workflows: { testWorkflow },
})
Referencing a workflowDirect link to Referencing a workflow
You can run workflows from agents, tools, the Mastra Client, or the command line. Get a reference by calling .getWorkflow() on your mastra or mastraClient instance, depending on your setup:
const testWorkflow = mastra.getWorkflow('testWorkflow')
mastra.getWorkflow() is preferred over a direct import for two reasons:
- It provides access to the Mastra instance configuration (logger, telemetry, storage, registered agents, and vector stores)
- It provides full TypeScript type inference for workflow input and output schemas
Note: Use getWorkflow() with the workflow's registration key (the key used when adding it to Mastra). While getWorkflowById() is available for retrieving workflows by their id property, it does not provide the same level of type inference.
Running workflowsDirect link to Running workflows
Workflows can be run in two modes: start waits for all steps to complete before returning, and stream emits events during execution. Choose the approach that fits your use case: start when you only need the final result, and stream when you want to monitor progress or trigger actions as steps complete.
- Start
- Stream
Create a workflow run instance using createRun(), then call .start() with inputData matching the workflow's inputSchema. The workflow executes all steps and returns the final result.
const run = await testWorkflow.createRun()
const result = await run.start({
inputData: {
message: 'Hello world',
},
})
if (result.status === 'success') {
console.log(result.result)
}
Create a workflow run instance using .createRun(), then call .stream() with inputData matching the workflow's inputSchema. Iterate over fullStream to track progress, then await result to get the final workflow result.
const run = await testWorkflow.createRun()
const stream = run.stream({
inputData: {
message: 'Hello world',
},
})
for await (const chunk of stream.fullStream) {
console.log(chunk)
}
// Get the final result (same type as run.start())
const result = await stream.result
if (result.status === 'success') {
console.log(result.result)
}
Workflow result typeDirect link to Workflow result type
Both run.start() and stream.result return a discriminated union based on the status property, which can be success, failed, suspended, tripwire, or paused. You can always safely access result.status, result.input, result.steps, and optionally result.state regardless of the status.
Additionally, depending on the status, different properties are available:
| Status | Unique properties | Description |
|---|---|---|
success | result | The workflow's output data |
failed | error | The error that caused the failure |
tripwire | tripwire | Contains reason, retry?, metadata?, processorId? |
suspended | suspendPayload, suspended | Suspension data and array of suspended step paths |
paused | (none) | Only common properties available |
To access status-specific properties, check the status first:
const result = await run.start({ inputData: { message: 'Hello world' } })
if (result.status === 'success') {
console.log(result.result) // Only available when status is "success"
} else if (result.status === 'failed') {
console.log(result.error.message)
} else if (result.status === 'suspended') {
console.log(result.suspendPayload)
}
Workflow outputDirect link to Workflow output
Here's an example of a successful workflow result, showing the input, steps, and result properties:
{
"status": "success",
"steps": {
"step-1": {
"status": "success",
"payload": {
"message": "Hello world"
},
"output": {
"formatted": "HELLO WORLD"
}
},
"step-2": {
"status": "success",
"payload": {
"formatted": "HELLO WORLD"
},
"output": {
"emphasized": "HELLO WORLD!!!"
}
}
},
"input": {
"message": "Hello world"
},
"result": {
"emphasized": "HELLO WORLD!!!"
}
}
Restarting active workflow runsDirect link to Restarting active workflow runs
When a workflow run loses connection to the server, it can be restarted from the last active step. This is useful for long-running workflows that might still be running when the server loses connection. Restarting a workflow run will resume execution from the last active step, and the workflow will continue from there.
Restarting all active workflow runs of a workflow with restartAllActiveWorkflowRuns()Direct link to restarting-all-active-workflow-runs-of-a-workflow-with-restartallactiveworkflowruns
Use restartAllActiveWorkflowRuns() to restart all active workflow runs of a workflow. This helps restart all active workflow runs of a workflow, without having to manually loop through each run and restart.
workflow.restartAllActiveWorkflowRuns()
Restarting an active workflow run with restart()Direct link to restarting-an-active-workflow-run-with-restart
Use restart() to restart an active workflow run from the last active step. This will resume execution from the last active step, and the workflow will continue from there.
const run = await workflow.createRun()
const result = await run.start({ inputData: { value: 'initial data' } })
const restartedResult = await run.restart()
Identifying active workflow runsDirect link to Identifying active workflow runs
When a workflow run is active, it will have a status of running or waiting. You can check the workflow's status to confirm it's active, and use active to identify the active workflow run.
const activeRuns = await workflow.listActiveWorkflowRuns()
if (activeRuns.runs.length > 0) {
console.log(activeRuns.runs)
}
When running the local mastra server, all active workflow runs will be restarted automatically when the server starts.
Using RequestContextDirect link to using-requestcontext
Use RequestContext to access request-specific values. This lets you conditionally adjust behavior based on the context of the request.
export type UserTier = {
'user-tier': 'enterprise' | 'pro'
}
const step1 = createStep({
execute: async ({ requestContext }) => {
const userTier = requestContext.get('user-tier') as UserTier['user-tier']
const maxResults = userTier === 'enterprise' ? 1000 : 50
return { maxResults }
},
})
Visit Request Context for more information.
For type-safe request context schema validation, see Schema Validation.
Testing with StudioDirect link to Testing with Studio
Use Studio to easily run workflows with different inputs, visualize the execution lifecycle, see the inputs and outputs for each step, and inspect each part of the workflow in more detail.
RelatedDirect link to Related
For a closer look at workflows, see our Workflow Guide, which walks through the core concepts with a practical example.