Parallel Execution with Steps
When building AI applications, you often need to process multiple independent tasks simultaneously to improve efficiency.
Control Flow DiagramDirect link to Control Flow Diagram
This example shows how to structure a workflow that executes steps in parallel, with each branch handling its own data flow and dependencies.
Here's the control flow diagram:
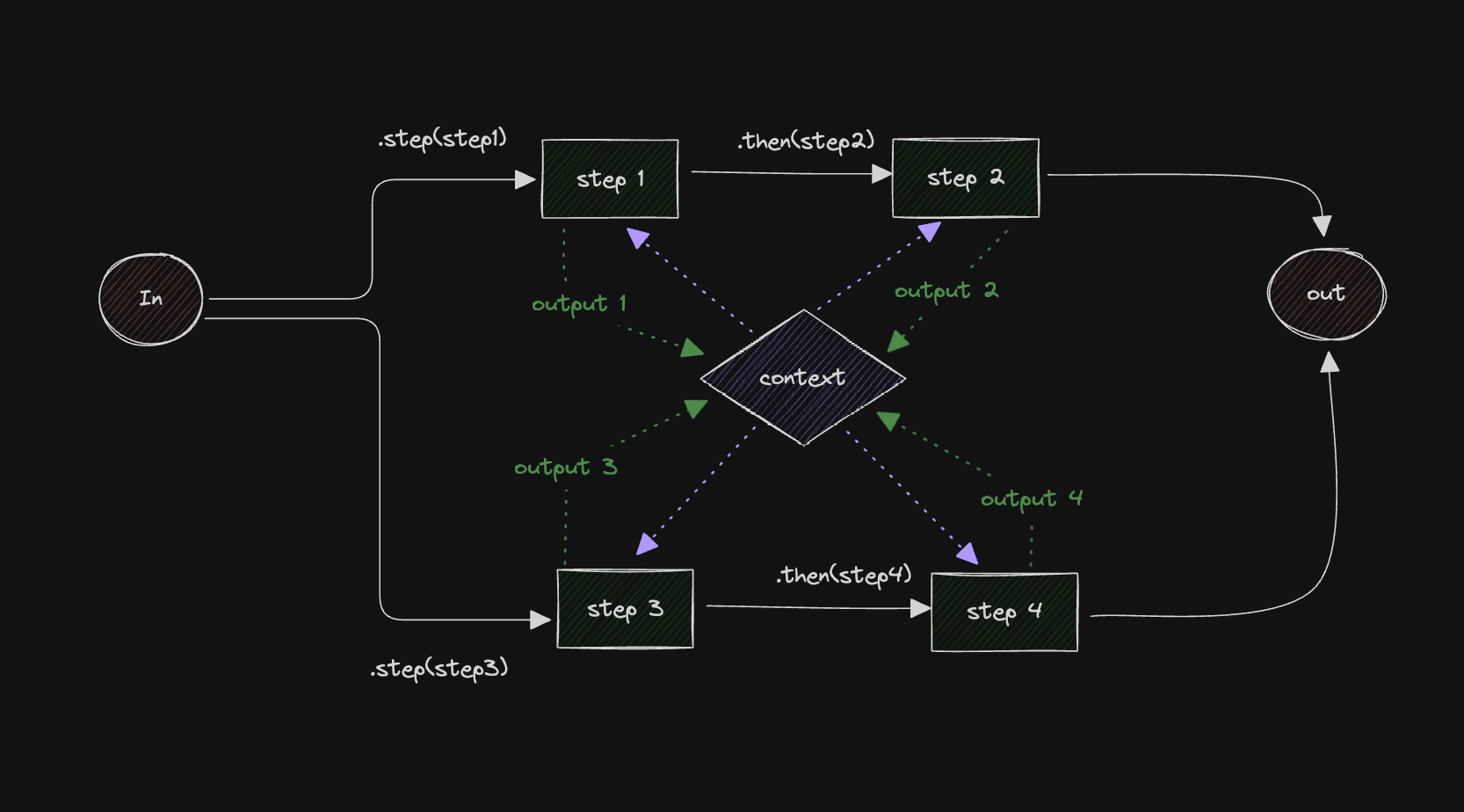
Creating the StepsDirect link to Creating the Steps
Let's start by creating the steps and initializing the workflow.
import { LegacyStep, LegacyWorkflow } from "@mastra/core/workflows/legacy";
import { z } from "zod";
const stepOne = new LegacyStep({
id: "stepOne",
execute: async ({ context }) => ({
doubledValue: context.triggerData.inputValue * 2,
}),
});
const stepTwo = new LegacyStep({
id: "stepTwo",
execute: async ({ context }) => {
if (context.steps.stepOne.status !== "success") {
return { incrementedValue: 0 };
}
return { incrementedValue: context.steps.stepOne.output.doubledValue + 1 };
},
});
const stepThree = new LegacyStep({
id: "stepThree",
execute: async ({ context }) => ({
tripledValue: context.triggerData.inputValue * 3,
}),
});
const stepFour = new LegacyStep({
id: "stepFour",
execute: async ({ context }) => {
if (context.steps.stepThree.status !== "success") {
return { isEven: false };
}
return { isEven: context.steps.stepThree.output.tripledValue % 2 === 0 };
},
});
const myWorkflow = new LegacyWorkflow({
name: "my-workflow",
triggerSchema: z.object({
inputValue: z.number(),
}),
});
Chaining and Parallelizing StepsDirect link to Chaining and Parallelizing Steps
Now we can add the steps to the workflow. Note the .then() method is used to chain the steps, but the .step() method is used to add the steps to the workflow.
myWorkflow
.step(stepOne)
.then(stepTwo) // chain one
.step(stepThree)
.then(stepFour) // chain two
.commit();
const { start } = myWorkflow.createRun();
const result = await start({ triggerData: { inputValue: 3 } });
View source on GitHub
Workflows (Legacy)Direct link to Workflows (Legacy)
The following links provide example documentation for legacy workflows:
- Creating a Simple Workflow (Legacy)
- Workflow (Legacy) with Sequential Steps
- Branching Paths
- Workflow (Legacy) with Conditional Branching (experimental)
- Calling an Agent From a Workflow (Legacy)
- Tool as a Workflow step (Legacy)
- Workflow (Legacy) with Cyclical dependencies
- Data Mapping with Workflow Variables (Legacy)
- Human in the Loop Workflow (Legacy)
- Workflow (Legacy) with Suspend and Resume