Using Agents
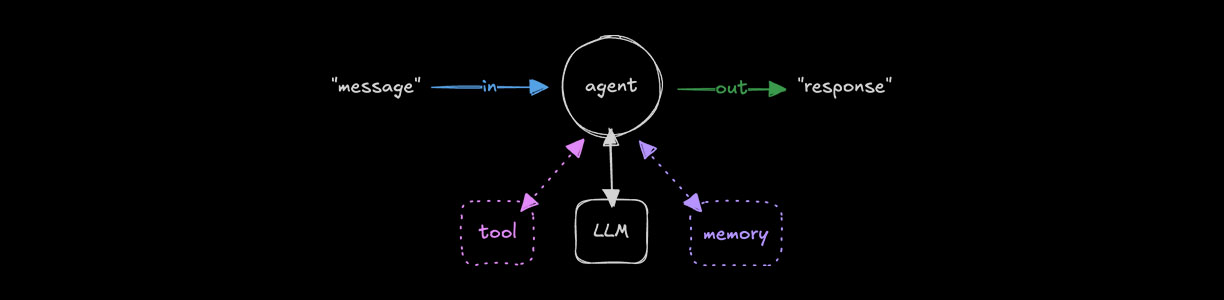
Agents use LLMs and tools to solve open-ended tasks. They reason about goals, decide which tools to use, retain conversation memory, and iterate internally until the model emits a final answer or an optional stop condition is met. Agents produce structured responses you can render in your UI or process programmatically. Use agents directly or compose them into workflows or agent networks.
An introduction to agents, and how they compare to workflows on YouTube (7 minutes)
Setting up agentsDirect link to Setting up agents
- Model router
- Vercel AI SDK
Add the Mastra core package to your project:
npm install @mastra/coreMastra's model router auto-detects environment variables for your chosen provider. For OpenAI, set
OPENAI_API_KEY:.envOPENAI_API_KEY=<your-api-key>noteMastra supports more than 600 models. Choose from the full list.
Create an agent by instantiating the
Agentclass with systeminstructionsand amodel:src/mastra/agents/test-agent.tsimport { Agent } from "@mastra/core/agent";
export const testAgent = new Agent({
name: "test-agent",
instructions: "You are a helpful assistant.",
model: "openai/gpt-4o-mini",
});
Include the Mastra core package alongside the Vercel AI SDK provider you want to use:
npm install @mastra/core @ai-sdk/openaiSet the corresponding environment variable for your provider. For OpenAI via the AI SDK:
.envOPENAI_API_KEY=<your-api-key>noteSee the AI SDK Providers in the Vercel AI SDK docs for additional configuration options.
To create an agent in Mastra, use the
Agentclass. Every agent must includeinstructionsto define its behavior, and amodelparameter to specify the LLM provider and model. When using the Vercel AI SDK, provide the client to your agent'smodelfield:src/mastra/agents/test-agent.tsimport { openai } from "@ai-sdk/openai";
import { Agent } from "@mastra/core/agent";
export const testAgent = new Agent({
name: "test-agent",
instructions: "You are a helpful assistant.",
model: openai("gpt-4o-mini"),
});
Instruction formatsDirect link to Instruction formats
Instructions define the agent's behavior, personality, and capabilities. They are system-level prompts that establish the agent's core identity and expertise.
Instructions can be provided in multiple formats for greater flexibility. The examples below illustrate the supported shapes:
// String (most common)
instructions: "You are a helpful assistant.";
// Array of strings
instructions: [
"You are a helpful assistant.",
"Always be polite.",
"Provide detailed answers.",
];
// Array of system messages
instructions: [
{ role: "system", content: "You are a helpful assistant." },
{ role: "system", content: "You have expertise in TypeScript." },
];
Provider-specific optionsDirect link to Provider-specific options
Each model provider also enables a few different options, including prompt caching and configuring reasoning. We provide a providerOptions flag to manage these. You can set providerOptions on the instruction level to set different caching strategy per system instruction/prompt.
// With provider-specific options (e.g., caching, reasoning)
instructions: {
role: "system",
content:
"You are an expert code reviewer. Analyze code for bugs, performance issues, and best practices.",
providerOptions: {
openai: { reasoningEffort: "high" }, // OpenAI's reasoning models
anthropic: { cacheControl: { type: "ephemeral" } } // Anthropic's prompt caching
}
}
See the Agent reference doc for more information.
Registering an agentDirect link to Registering an agent
Register your agent in the Mastra instance to make it available throughout your application. Once registered, it can be called from workflows, tools, or other agents, and has access to shared resources such as memory, logging, and observability features:
import { Mastra } from "@mastra/core/mastra";
import { testAgent } from "./agents/test-agent";
export const mastra = new Mastra({
// ...
agents: { testAgent },
});
Calling an agentDirect link to Calling an agent
You can call agents from workflow steps, tools, or the Mastra Client. Get a reference by calling .getAgent() on your mastra or mastraClient instance, depending on your setup:
const testAgent = mastra.getAgent("testAgent");
mastra.getAgent() is preferred over directly importing an agent in to your file, since it provides access to the Mastra instance configuration (logger, telemetry, storage, registered agents, and vector stores).
From a workflow stepDirect link to From a workflow step
The mastra instance is passed as an argument to a workflow step’s execute function. It provides access to registered agents using getAgent(). Use this method to retrieve your agent, then call generate() with a prompt.
const step1 = createStep({
// ...
execute: async ({ mastra }) => {
const agent = mastra.getAgent("testAgent");
const response = await agent.generate("Help me organize my day");
console.log(response.text);
}
});
From a toolDirect link to From a tool
The mastra instance is available within a tool’s execute function. Use getAgent() to retrieve a registered agent and call generate() with a prompt.
export const testTool = createTool({
// ...
execute: async ({ mastra }) => {
const agent = mastra.getAgent("testAgent");
const response = await agent.generate("Help me organize my day");
console.log(response!.text);
}
});
Using HTTP or curlDirect link to Using HTTP or curl
You can interact with a registered agent by sending a POST request to your Mastra application's /generate endpoint. Include a messages array of role/content pairs.
curl -X POST http://localhost:4111/api/agents/testAgent/generate \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "Help me organize my day"
}
]
}'| jq -r '.text'
Example output
1. What time do you plan to start your day?
2. Do you have any specific tasks or appointments scheduled for today?
3. Are there any personal goals or activities you want to include (e.g., exercise, reading, hobbies)?
4. How much time do you want to allocate for work versus personal time?
5. Do you have any deadlines or priorities that need to be addressed?
Generating responsesDirect link to Generating responses
Agents can return results in two ways: generating the full output before returning it or streaming tokens in real time. Choose the approach that fits your use case: generate for short, internal responses or debugging, and stream to deliver pixels to end users as quickly as possible.
- Generate
- Stream
Pass a single string for simple prompts, an array of strings when providing multiple pieces of context, or an array of message objects with role and content.
(The role defines the speaker for each message. Typical roles are user for human input, assistant for agent responses, and system for instructions.)
const response = await testAgent.generate([
{ role: "user", content: "Help me organize my day" },
{ role: "user", content: "My day starts at 9am and finishes at 5.30pm" },
{ role: "user", content: "I take lunch between 12:30 and 13:30" },
{
role: "user",
content: "I have meetings Monday to Friday between 10:30 and 11:30",
},
]);
console.log(response.text);
Pass a single string for simple prompts, an array of strings when providing multiple pieces of context, or an array of message objects with role and content.
(The role defines the speaker for each message. Typical roles are user for human input, assistant for agent responses, and system for instructions.)
const stream = await testAgent.stream([
{ role: "user", content: "Help me organize my day" },
{ role: "user", content: "My day starts at 9am and finishes at 5.30pm" },
{ role: "user", content: "I take lunch between 12:30 and 13:30" },
{
role: "user",
content: "I have meetings Monday to Friday between 10:30 and 11:30",
},
]);
for await (const chunk of stream.textStream) {
process.stdout.write(chunk);
}
Completion using onFinish()Direct link to completion-using-onfinish
When streaming responses, the onFinish() callback runs after the LLM finishes generating its response and all tool executions are complete.
It provides the final text, execution steps, finishReason, token usage statistics, and other metadata useful for monitoring or logging.
const stream = await testAgent.stream("Help me organize my day", {
onFinish: ({ steps, text, finishReason, usage }) => {
console.log({ steps, text, finishReason, usage });
},
});
for await (const chunk of stream.textStream) {
process.stdout.write(chunk);
}
See .generate() or .stream() for more information.
Structured outputDirect link to Structured output
Agents can return structured, type-safe data by defining the expected output using either Zod or JSON Schema. We recommend Zod for better TypeScript support and developer experience. The parsed result is available on response.object, allowing you to work directly with validated and typed data.
Using ZodDirect link to Using Zod
Define the output shape using Zod:
import { z } from "zod";
const response = await testAgent.generate(
[
{
role: "system",
content: "Provide a summary and keywords for the following text:",
},
{
role: "user",
content: "Monkey, Ice Cream, Boat",
},
],
{
structuredOutput: {
schema: z.object({
summary: z.string(),
keywords: z.array(z.string()),
}),
},
},
);
console.log(response.object);
Structuring sub agentDirect link to Structuring sub agent
Use the model property to have a separate agent generate the structured output for you.
import { z } from "zod";
const response = await testAgentWithTools.generate(
[
{
role: "system",
content: "Provide a summary and keywords for the following text:",
},
{
role: "user",
content: "Please use your test tool and let me know the results",
},
],
{
structuredOutput: {
schema: z.object({
summary: z.string(),
keywords: z.array(z.string()),
}),
model: "openai/gpt-4o",
},
},
);
console.log(response.object);
console.log(response.toolResults);
Response formatDirect link to Response format
By default structuredOutput will use response_format to pass the schema to the model provider. If the model provider does not natively support response_format it's possible that this will error or not give the desired results. To keep using the same model use jsonPromptInjection to bypass response format and inject a system prompt message to coerce the model to return structured output.
import { z } from "zod";
const response = await testAgentThatDoesntSupportStructuredOutput.generate(
[
{
role: "system",
content: "Provide a summary and keywords for the following text:",
},
{
role: "user",
content: "Monkey, Ice Cream, Boat",
},
],
{
structuredOutput: {
schema: z.object({
summary: z.string(),
keywords: z.array(z.string()),
}),
jsonPromptInjection: true,
},
},
);
console.log(response.object);
Gemini 2.5 models do not support combining response_format (structured output) with function calling (tools) in the same API call. If your agent has tools and you're using structuredOutput with a Gemini 2.5 model, you must set jsonPromptInjection: true to avoid the error Function calling with a response mime type: 'application/json' is unsupported.
const response = await agentWithTools.generate("Your prompt", {
structuredOutput: {
schema: yourSchema,
jsonPromptInjection: true, // Required for Gemini 2.5 when tools are present
},
});
Using toolsDirect link to Using tools
Agents can use tools to go beyond language generation, enabling structured interactions with external APIs and services. Tools allow agents to access data and perform clearly defined operations in a reliable, repeatable way.
export const testAgent = new Agent({
// ...
tools: { testTool },
});
See Using Tools for more information.
Using RuntimeContextDirect link to using-runtimecontext
Use RuntimeContext to access request-specific values. This lets you conditionally adjust behavior based on the context of the request.
export type UserTier = {
"user-tier": "enterprise" | "pro";
};
export const testAgent = new Agent({
// ...
model: ({ runtimeContext }) => {
const userTier = runtimeContext.get("user-tier") as UserTier["user-tier"];
return userTier === "enterprise"
? openai("gpt-4o-mini")
: openai("gpt-4.1-nano");
},
});
See Runtime Context for more information.
Using maxStepsDirect link to using-maxsteps
The maxSteps parameter controls the maximum number of sequential LLM calls an agent can make. Each step includes generating a response, executing any tool calls, and processing the result. Limiting steps helps prevent infinite loops, reduce latency, and control token usage for agents that use tools. The default is 5, but can be increased:
const response = await testAgent.generate("Help me organize my day", {
maxSteps: 10,
});
console.log(response.text);
Using onStepFinishDirect link to using-onstepfinish
You can monitor the progress of multi-step operations using the onStepFinish callback. This is useful for debugging or providing progress updates to users.
onStepFinish is only available when streaming or generating text without structured output.
const response = await testAgent.generate("Help me organize my day", {
onStepFinish: ({ text, toolCalls, toolResults, finishReason, usage }) => {
console.log({ text, toolCalls, toolResults, finishReason, usage });
},
});
Working with imagesDirect link to Working with images
Agents can analyze and describe images by processing both the visual content and any text within them. To enable image analysis, pass an object with type: 'image' and the image URL in the content array. You can combine image content with text prompts to guide the agent's analysis.
const response = await testAgent.generate([
{
role: "user",
content: [
{
type: "image",
image: "https://placebear.com/cache/395-205.jpg",
mimeType: "image/jpeg",
},
{
type: "text",
text: "Describe the image in detail, and extract all the text in the image.",
},
],
},
]);
console.log(response.text);
Testing with StudioDirect link to Testing with Studio
Use Studio to test agents with different messages, inspect tool calls and responses, and debug agent behavior.