Deploy in a Monorepo
Deploying Mastra in a monorepo follows the same process as a standalone application. This guide covers monorepo-specific considerations. For the core build and deployment steps, see Deploy a Mastra Server.
Supported monoreposDirect link to Supported monorepos
Mastra works with:
- npm workspaces
- pnpm workspaces
- Yarn workspaces
- Turborepo
Known limitations:
- Bun workspaces - partial support; known issues
- Nx - You can use Nx's supported dependency strategies but you need to have
package.jsonfiles inside your workspace packages
Example structureDirect link to Example structure
In this example, the Mastra application is located at apps/api:
apps/
├── api/
│ ├── src/
│ │ └── mastra/
│ │ ├── agents/
│ │ ├── tools/
│ │ ├── workflows/
│ │ └── index.ts
│ ├── package.json
│ └── tsconfig.json
└── web/
packages/
├── ui/
└── utils/
package.json
Building from a monorepoDirect link to Building from a monorepo
Use your monorepo tool to run the build command from the correct package. There's no need for special flags.
Examples:
- npm
- pnpm
- yarn
- Turborepo
npm run build --workspace=apps/api
pnpm --filter api run build
yarn workspace api build
turbo run build --filter=api
Your package's build script should run mastra build:
{
"scripts": {
"build": "mastra build"
}
}
Workspace packagesDirect link to Workspace packages
When your Mastra application imports from other workspace packages, Mastra handles this automatically:
- If the package is pre-compiled (e.g., built with
tscortsdown), Mastra imports the compiled JavaScript - If the package contains uncompiled TypeScript, Mastra transpiles it during the build
For most setups, this works without configuration. If you encounter issues with workspace package imports, add the package to transpilePackages:
export const mastra = new Mastra({
bundler: {
transpilePackages: ["@my-org/utils"],
},
});
Environment variablesDirect link to Environment variables
Store .env files in the Mastra application directory (e.g., apps/api/.env), not the monorepo root.
Deployment configurationDirect link to Deployment configuration
When deploying to cloud providers, ensure the correct package is selected as the deploy target. Selecting the monorepo root instead of the application directory (e.g., apps/api) is a common mistake.
Most providers let you specify the root directory in their dashboard or configuration file.
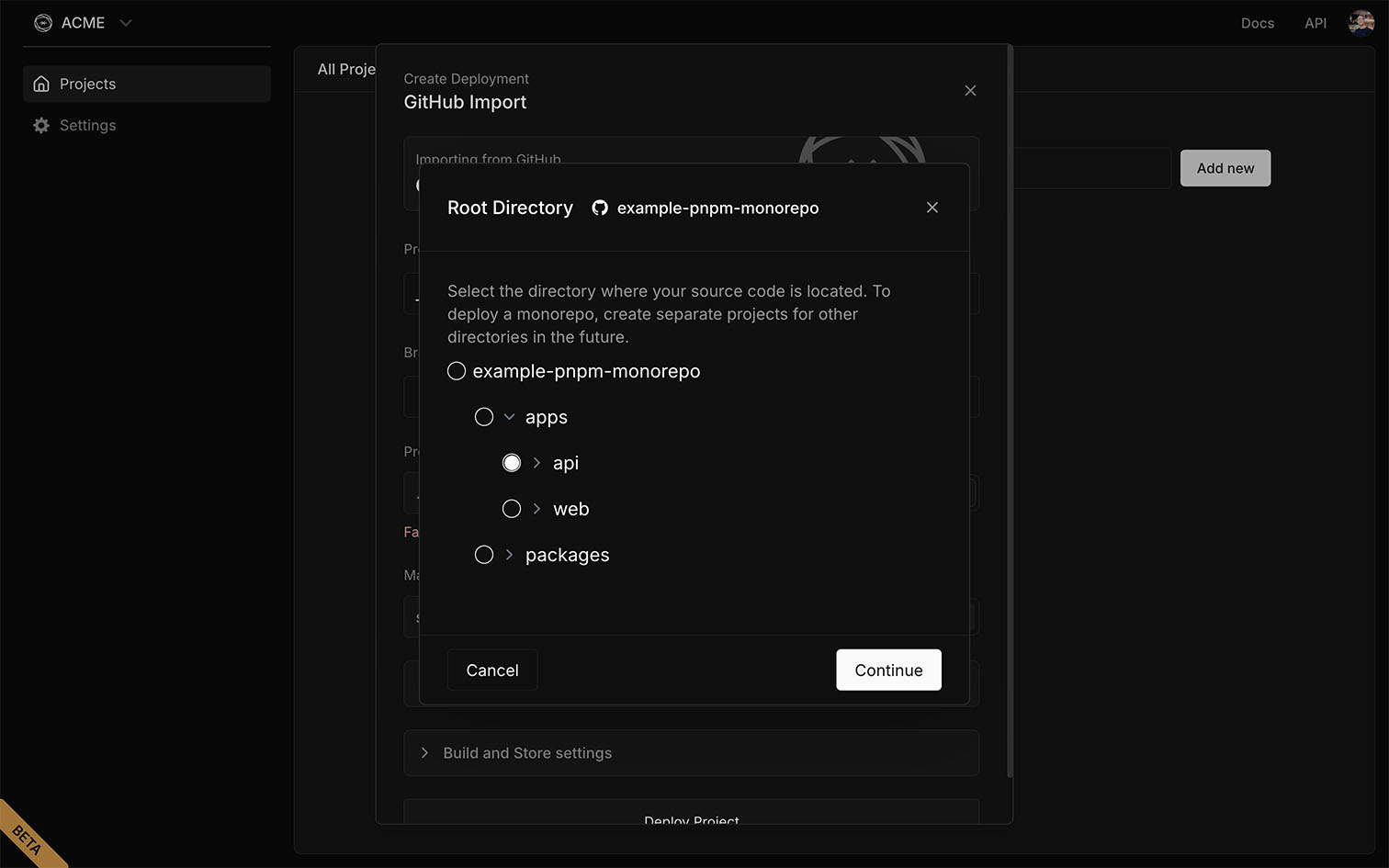
Mastra CloudDirect link to Mastra Cloud
The image below shows how to select apps/api as the project root when deploying to Mastra Cloud. While the interface may differ between providers, the configuration remains the same.
Dependency managementDirect link to Dependency management
Keep dependencies consistent to avoid version conflicts and build errors:
- Use a single lockfile at the monorepo root so all packages resolve the same versions
- Align versions of shared libraries (like Mastra or frameworks) to prevent duplicates
TroubleshootingDirect link to Troubleshooting
Workspace package not foundDirect link to Workspace package not found
If Mastra can't resolve a workspace package, ensure:
- The package is listed in your
package.jsondependencies - Your lockfile is up to date (
pnpm install,npm install, etc.) - The package has a valid
mainorexportsfield in itspackage.json
TypeScript errors from workspace packagesDirect link to TypeScript errors from workspace packages
If you see type errors from uncompiled workspace packages, either:
- Build the package first (recommended for faster Mastra builds)
- Add the package to
transpilePackagesin your Mastra config
RelatedDirect link to Related
- Deploy a Mastra Server - Core build and deployment guide
- Configuration Reference -
bundler.transpilePackagesand other options - CLI Reference - Build command flags